About SSO Services, It's Meaning and How Does It Work?, FAQs

Table of Content
About SSO Services, It's Meaning and How Does It Work?
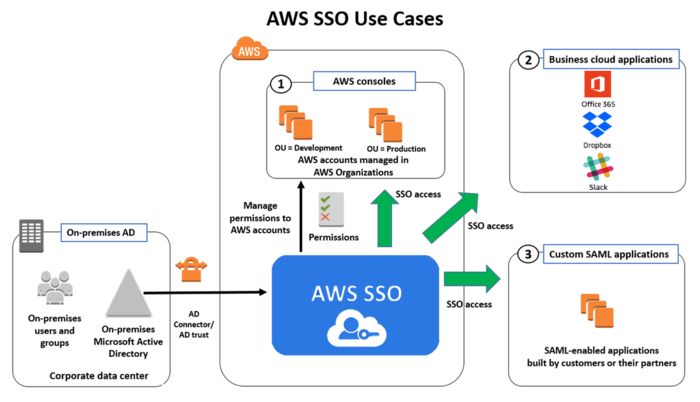
Sso Services, Through The Usage Of Single Sign-on (sso), Users Can Authenticate Themselves Once And Access Numerous Websites And Application
About SSO Services, It's Meaning and How Does It Work?, FAQs
SSO Services: Through the usage of single sign-on (SSO), users can authenticate themselves once and access numerous websites and applications. Organisations are giving priority to access control systems that enhance security and user experience since consumers often access applications straight from their browsers. Both benefits are provided by SSO, since after their identity has been verified, users can access all password-protected resources without having to log in again.
Why is SSO important?
There are various advantages for both individuals and organisations when user logins are streamlined with SSO.
 Why sso service is important
Why sso service is importantBolster the Security of Passwords
When SSO isn't used, users have to keep track of numerous passwords for various websites. This could result in security practices that are not advised, like using the same or basic passwords across multiple accounts. In addition, individuals may mistype or forget their login information when accessing a service. SSO keeps users from becoming tired of their passwords and motivates them to establish a strong password that works on a variety of websites.
Boost output
Workers frequently utilise multiple enterprise applications, each requiring a different kind of authentication. Entering the password and username by hand for each application takes time and is not productive. SSO facilitates protected resource access and expedites the user validation procedure for enterprise apps.
Cut Expenses
Enterprise users may lose track of their login information while trying to remember many passwords. The workload for the internal IT staff grows as a result of the frequent requests for password retrieval or resets. By reducing the likelihood of forgotten passwords, SSO implementation lowers the amount of support resources needed to handle password reset requests.
Boost Your Security Stance.
SSO offers strong access control to all kinds of data and makes user access audits easier by reducing the number of passwords needed for each user. In addition to assisting businesses in adhering to data security laws, this lowers the likelihood of security incidents that target passwords.
Boost the Quality of the Client Experience
SSO is used by cloud application providers to offer end users a smooth credential management and login process. While managing fewer passwords, users can still safely access the data and applications they require to carry out their daily tasks.
 SSO Service Cut Expenses
SSO Service Cut ExpensesHow does SSO Work?
SSO creates a trusting relationship between the application or service and an identity provider (IdP), which is another name for an external service provider. A centralised SSO service and the application engage in several communication, validation, and authentication processes to make this happen. The following list contains the main elements of SSO solutions.
SSO Assistance
Applications rely on a central service called an SSO service to authenticate users. An application will route an unauthenticated user to the SSO service if they try to access it. After authenticating, the service returns the user to the original application. Usually, a specialised SSO policy server powers the service.
SSO Currency
A digital file including user-identifying data, like a username or email address, is called an SSO token. An application exchanges an SSO token with the SSO service to authenticate a user when the user requests access to the application.
SSO Process
The following is the SSO procedure:
- An application creates an SSO token and makes an authentication request to the SSO service when a user logs in.
- The service determines whether the user has already received system authentication. If so, it notifies the programme to provide access to the user by sending an authentication-confirmed response.
- The SSO service leads the user to a central login page and requests their username and password if they do not have a verified credential.
- After submission, the application receives a good answer from the service after verifying the user credentials.
- If not, the user gets an error message and has to enter their login information again. If a user makes several unsuccessful attempts to log in, the service may ban them from making any more attempts.
 SSO Service works
SSO Service worksWhat are the Types of SSO?
SSO systems verify and authenticate user credentials using a variety of standards and protocols.
SAML
Applications communicate authentication details with the SSO service via a protocol or set of rules called SAML, or Security Assertion Markup Language. Browser-friendly markup language XML is used by SAML to transmit user identity information. Because SAML-based SSO services do not need apps to retain user credentials on their system, they offer improved security and flexibility.
OAuth
Open Authorization, or OAuth, is an open standard that enables apps to safely obtain user data from other websites without requiring a password. Applications utilise OAuth to obtain user permission to access password-protected data rather than asking for user passwords. Through APIs, OAuth builds application trust, enabling applications to make and receive authentication requests inside a predefined framework.
OIDC
Using a single set of login credentials to visit numerous websites is possible with OIDC OpenID. It permits the service provider to take on the responsibility of user credential authentication. Web applications utilise OIDC to request more data and verify the user’s identity rather than sending an authentication token to a third-party identity service.
Kerberos
With the use of a ticket-based authentication system called Kerberos, several parties can mutually confirm their identities via a network. To stop illegal access to identification data sent between the server, clients, and Key Distribution Centre, security cryptography is used.
Is SSO Secure?
SSO is a sophisticated and well-liked identity access management system, yes. When implemented, a single sign-on solution aids in the administration of user access for enterprise resources and applications within organisations. Setting and remembering strong passwords is made easier for application users by an SSO solution. The SSO technology also allows the IT team to monitor user behaviour, enhance system resilience, and lower security concerns.
 Is SSO Service Secure or Not
Is SSO Service Secure or NotHow does SSO compare with other access management solutions?
Depending on your needs, you have a variety of identity and access management options to select from.
Centralised Identity Administration
A digital architecture called federated identity management (FIM) enables the sharing, management, and authentication of user identities across various apps from various suppliers. With FIM, for instance, employees may log in to one application and use multiple enterprise apps without having to log in again. Using a reliable identity source, FIM verifies the credentials that the service provider submitted.
Federated Identity Management Versus SSO
For cross-domain applications, federated identity management offers a complete identity authentication and management solution. In the meantime, the FIM model has a special feature called single sign-on (SSO). SSO is restricted to services or apps hosted by a single vendor, but FIM enables users to access services from several vendors with a single login.
Same login
Same sign-on, commonly known by its acronym, is a digital solution that keeps user credentials updated and synchronised across all of the devices that the user accesses. Password vaults and password managers work similarly, enabling users to sign in to numerous apps on various devices without having to remember their login credentials.
Single sign-on vs. Same Sign-On
Users must authenticate themselves once for single sign-on systems. After logging in, the user doesn’t need to authenticate again to access other web apps and services. Simultaneously, the same sign-on necessitates that the user re-enters their login credentials each time.
Multi-Factor Authentication
A user authentication framework that uses two or more technologies to confirm the user’s identity is known as multi-factor authentication. For instance, to allow secure access, users input their email address, password, and one-time password (OTP) that is texted to their mobile device on a website.
Multi-factor Authentication Versus SSO
SSO makes it easier for businesses to implement stronger password security measures by enabling access to all connected services with a single login. Added security layers offered by multi-factor authentication lessen the chance of unwanted access via credential theft. Web applications can be made more secure by integrating multi-factor authentication and SSO.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Using a single set of login credentials, users can access numerous applications and websites through single sign-on (SSO) identification methods. SSO makes the user authentication procedure more efficient.
By enabling customers, partners, and contractors to authenticate just once and gain safe access to numerous digital services and apps, Single Sign-On (SSO) streamlines the login process for users.
SSO can enhance security by reducing the number of passwords users need to manage and by centralizing authentication processes. However, it requires careful implementation and adherence to security best practices to mitigate risks associated with potential single points of failure.
While SSO can provide significant benefits, its suitability depends on factors such as organizational size, IT infrastructure, security requirements, and user needs. Small businesses to large enterprises can implement SSO solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
Start by assessing your organization's authentication needs, evaluating different SSO solutions and providers, and planning for integration with existing systems. Engaging with an experienced SSO provider or consultant can also streamline the implementation process.